LCC在TAC2014上的两项任务中成绩非常好,由于它是一个企业,所以比较务实,对待任务的处理方法上比较切合实际应用,值得认真读一下他们的实验论文。
###Introduction
介绍EDL(Entity Detection and Linking)和EAE(Event Argument Extraction)
The EDL task builds on the fact that **the basic entries in our knowledge base are named entities**. Across a corpus of documents, the same entity may be mentioned multiple times, and moreover, not all mentions of the same name may refer to the same entry in the KB. Sometimes, the same entity is referred to by different names, i.e. synonymy. Other times, the same name can refer to several different entities, i.e. polysemy. For example, “Bank of America” and “BoA” can refer to the same entry, but “BoA” can also refer to a Korean pop star.
EDL任务的原因是由于我们知识库的基础是命名实体。而一个实体 可能会提到多次,但是他们不见得是同一个意思,因为还有同义词和多义词。
KB可以被pre-populated,通过一个已知的数据源,例如Wikipedia,来识别句子中的实体那些已经在已知数据源中。如果有的实体并不在其中,那就是NIL实体。如何自动的识别NIL实体跟哪些实体是同义的并把它们聚类在一起,也是很重要的。
于是,EDL不仅是链接文档中的实体,聚类实体,还要抽取这些实体。
EAE是EDL的扩展,检测实体参与的事件。
The EAE task expands the KB, which has been populated with entities from text, by detecting the events in which the entities participate. Events are more complex forms of knowledge, which have a variety of arguments and attributes including par- ticipants, temporal and spatial groundings, modal- ities, frequencies of occurrence, etc.
###Entity Detection and Linking
EDL的目的:
- 从文中找到与KB项相关的实体
- 从NIL实体中创造新的KB项
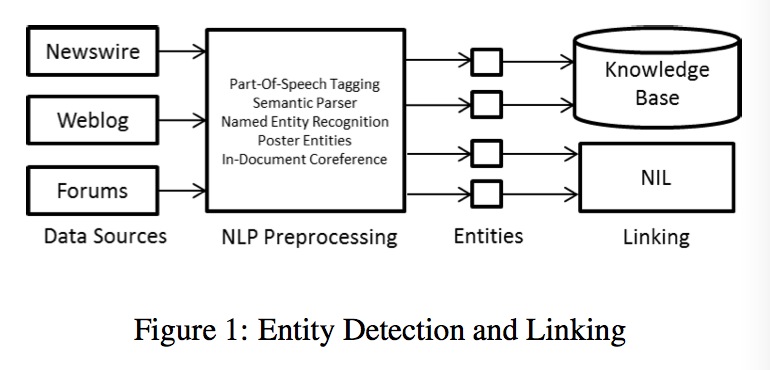
处理流程如上图,具体步骤:
- 将不同的数据源转为文本,对于blog和论坛的数据,把发帖人信息保留
- 各种NLP工具处理文本,如词性标注、语义解析、命名实体识别、文档内协同关系(IDC),输出识别出的命名实体。
- 利用上面的命名实体,进行EDL或者NIL聚类
####Entity Recognition
对EDL来说,既要识别与KB项相关的潜在项,又要找到可能是新KB项的那些项。与传统命名实体识别的区别在于,它只要与已知KB项有关系的那些。
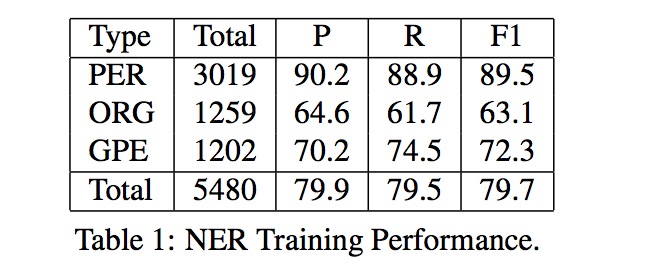
这项任务只考虑三类实体:PER(person),ORG(organizations)、GPE(geo-political entities)。
算法:
- Identify NER with CiceroLiteML
- Recognize spans of text from KB
- Filter entities that are not PER, ORG, and GPE
- Extract XML poster tags as known PER
- Detect acronyms / near edit distance to entities
具体内容:
- 利用Cicero-LiteML1系统来抽取命名实体。(**Which uses a supervised maximum entropy model combined with high-precision lexicons and gram- mars to recognize entities in text. **)
- 实现自己的entity linking系统来识别可能是命名实体的文字块,以及判断属于哪一类。
关于识别文字块,实现了自己的Surface Text to Entity Mapping(STEM)resource,包含了所有的wikipedia的链接信息。 对于这个resource中的每个string,都记录在wikipedia中出现的次数,以及链接哪个实体。而对于每一个实体,实现了自己的Wikipedia Resolved Article Type Selector (WRATS)2,可以将每一个wikipedia页面给一个语义类型。然后对于哪些潜在的实体,如果它的最大频次KB项不是PER/ORG/GPE之一,就被去掉。例如:“Grabo ́wka”在wiki中出现了80次,其中18次指向了同一个页面,而这18次都是GPE类型,这个词以后就被认为是GPE.
从XML抽取的信息,由于其带标签,准确率很高,就没有必要过WRATS部分。
最后,又搜了一遍已知名称的缩写、常见的错误拼写,因为论坛数据中很容易发生这些情况。
F-measure:79.7%
####Within-Document Coreference
Entities are often mentioned multiple times in the same documents, and recognizing this is referred to as within-document coreference (IDC)
由于一个文档内,可能会多次提到同一个KB,于是文档内的识别也很重要。例如,Johnson指一个British警官,而下文中的Alan Johnson应该也是同一个人。
同样对别称也做了Entity Linking。例如:先看见 Geoge Herman Ruth,然后在文中又看见了Babe,那么就可以确定作者指的是Babe Ruth。同样也对这部分做了缩写、错拼的检查。
IDC的准确率达到了95.1%
####Entity Linking
当识别完文档内的实体,就可以把实体关联起来,或者解决Nil实体。整个实体链接分为三步:Candidate generation, candidate ranking, NIL determination. 之前也描述过这个Entity Linking系统2和3,但这次的任务与之前的不太一样。
- 通过各种资源(STEM,网页,链接)从Wiki中找出潜在的KB项
- 用一个上下文模型来排序这些KB
- 应用一个启发式规则来判断一个KB项是否该留下还是该为NIL
最终,F值81.6%
###NIL Clustering
####Grapha partiation
####Similarity Model
采用LibLinear algorithm4
-
J. Lehmann, P. Aarseth, L. Nezda, S. Fayyaz, A. Jung, S. Monahan, and M. Oberoi. 2007. Language Computer Corporation’s ACE 2007 System Description. In Proceedings of 2007 Automatic Content Extraction Conference. ↩
-
J. Lehmann, S. Monahan, L. Nezda, A. Jung, and Y. Shi. 2010. LCC Approaches to Knowledge Base Popula- tion at TAC 2010. In Proceedings of 2010 Text Analy- sis Conference. ↩ ↩2
-
S. Monahan, J. Lehmann, T. Nyberg, J. Plymale, and A. Jung. 2011. Cross-Lingual Cross-Document Coreference with Entity Linking. In Proceedings of 2011 Text Analysis Conference. ↩
-
R.-E. Fan, K.-W. Chang, C.-J. Hsieh, X.-R. Wang, and C.-J. Lin. 2008. Liblinear: A library for large lin- ear classification. In Journal of Machine Learning Re- search 9, pages 1871–1874. ↩